Why are stock index futures and options called derivatives
Futures and derivatives are financial instruments that are used by companies and individuals to hedge risk. The risks may be anything that may carry an eventual financial liability and ranges from commodity prices to future revenues or catastrophic insurance losses.
Derivatives
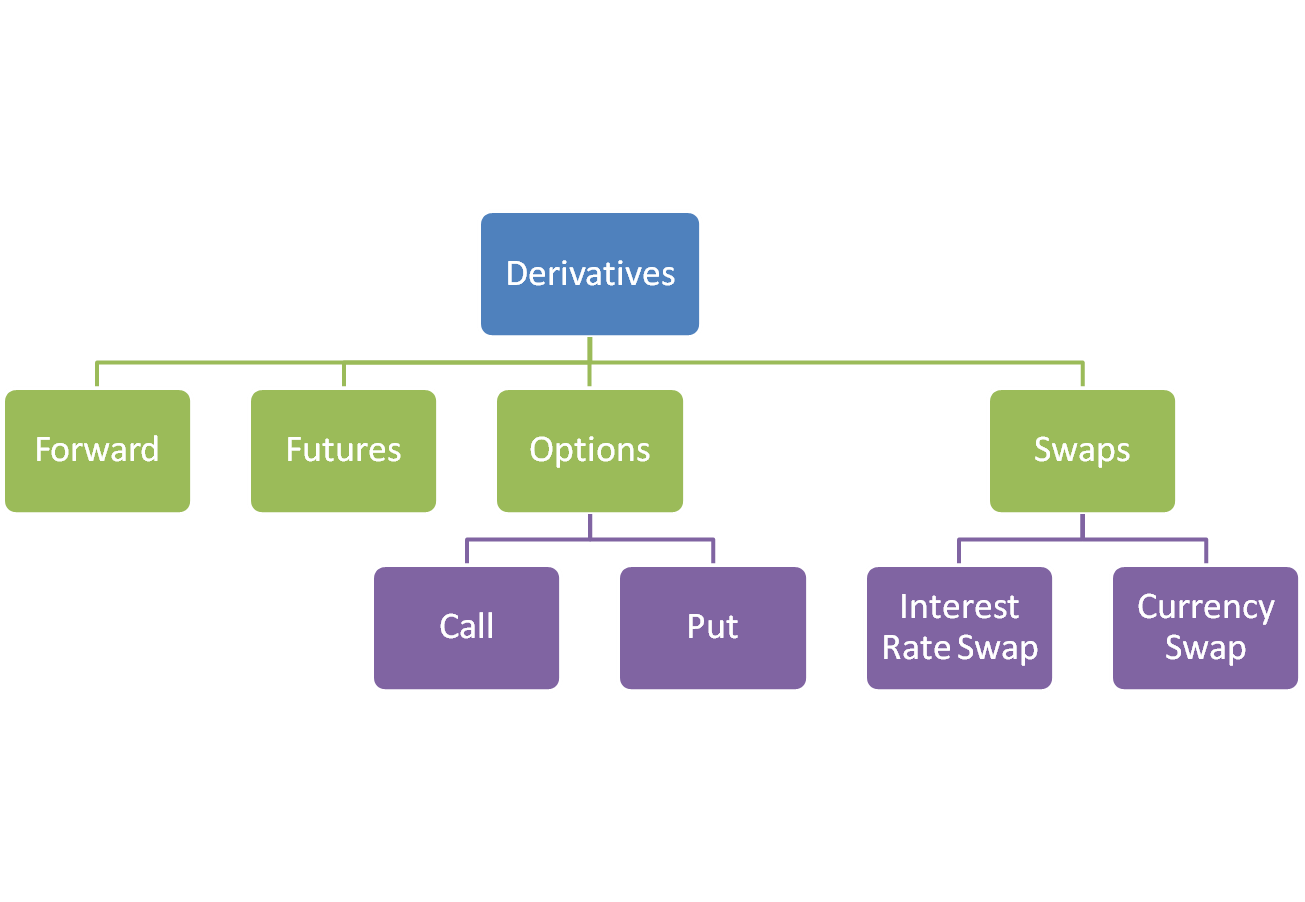
These risks are transferred to financially stronger companies or dealers who trade them on to make a profit. The main differences between futures and derivatives are in their regulation. Two parties agree in a futures contract to buy a tangible or intangible product or asset at a specified price and on a specified future date. The traded asset is called the underlying and may be a commodity, currency, interest rate, stock market index or catastrophic insurance loss.

The trade date is called the settlement or maturity date. The agreed price is called the futures price. Both parties are obligated to carry out the contract. Derivatives are contracts whose value derives from something else. It can be the variation over time of a commodity price, exchange rate, stock market index or bank deposit. It also could be the variation of a commodity price against a stock market index.
Technically speaking, a futures contract is a derivative. An option is a derivative contract where a seller offers a buyer the right, but not an obligation as in the case of futures, to buy an asset. They specify both the price, the strike price and the date, the exercise date, of the transaction. A swap is a derivative contract where two parties exchange cash flows, such as interest rate payments. The interest rate calculations are agreed and the two sides are obligated to the deal.
There are also combinations of swaps and options called "swaptions. Futures contracts are also called exchange-traded derivatives because of the location where they are traded. This is the main difference between them and other derivatives.
For example, gold or platinum futures are traded on futures exchanges like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange or the London Metal Exchange. The trades are conducted electronically, via telephone or by open outcry. In this way, the exchange minimizes the credit and counterparty risk and guarantees the financial integrity of the transaction.
In effect, the exchange is the counterparty to all trades. Options, swaps, swaptions and other derivatives that are traded through private agreements between two parties are called over-the-counter derivatives. A forward contract is a futures contract that is agreed privately between the parties and traded OTC.
The futures exchanges standardize futures contracts.
They define the underlying product or asset and whether it will be delivered in cash or physical kind. The exchanges also set margin requirements that are financial guarantees to ensure the contract obligations are fulfilled. There is no standardization of, or margin requirement for, OTC contracts.
Futures exchanges, like stock exchanges, are subject to financial regulation. OTC trading accounts for 95 percent of all derivatives trading and is unregulated. Based in London, Maria Kielmas worked in earthquake engineering and international petroleum exploration before entering journalism in She has written for the "Financial Times," "Barron's," "Christian Science Monitor," and "Rheinischer Merkur" as well as specialist publications on the energy and financial industries and the European, Middle Eastern, African, Asian and Latin American regions.
She has a Bachelor of Science in physics and geology from Manchester University and a Master of Science in marine geotechnics from the University of Wales School of Ocean Sciences. Each week, Zack's e-newsletter will address topics such as retirement, savings, loans, mortgages, tax and investment strategies, and more.
At the center of everything we do is a strong commitment to independent research and sharing its profitable discoveries with investors. This dedication to giving investors a trading advantage led to the creation of our proven Zacks Rank stock-rating system.
These returns cover a period from and were examined and attested by Baker Tilly, an independent accounting firm. Visit performance for information about the performance numbers displayed above.
Skip to main content.
What Is the Difference Between a Derivative and a Future? More Articles What Is a Credit Derivative? The Costs and Benefits of Organized Futures Markets Derivative Hedging Instruments What Is a Derivative Contract? Futures Two parties agree in a futures contract to buy a tangible or intangible product or asset at a specified price and on a specified future date.
Derivatives Derivatives are contracts whose value derives from something else. Futures Trading Futures contracts are also called exchange-traded derivatives because of the location where they are traded. OTC Trading Options, swaps, swaptions and other derivatives that are traded through private agreements between two parties are called over-the-counter derivatives.
Standardization The futures exchanges standardize futures contracts.
Hughes Optioneering
Regulation Futures exchanges, like stock exchanges, are subject to financial regulation. References 5 Institute for Financial Management: A Quick Guide to Derivatives State University of New York: Derivatives, Futures, Options and Swaps, Part 1 Harvard University: Regulation of OTC Derivatives Markets — EU vs US Initiatives.
Regulation on Over-The-Counter Derivatives and Markets Infrastructures — Guide Managed Futures Today: About the Author Based in London, Maria Kielmas worked in earthquake engineering and international petroleum exploration before entering journalism in Recommended Articles The Responsibilities of a Retirement Plan Fiduciary What Is a Group Annuity? What Is a Bear Futures Spread?
How to Stop a Loss on a Long-Term Futures Contract. Related Articles What Is a Derivative on Wall Street? Money Sense E-newsletter Each week, Zack's e-newsletter will address topics such as retirement, savings, loans, mortgages, tax and investment strategies, and more. The Advantages of Trading Options vs.
Futures Is There a Margin Call on Gold Options? Trending Topics Latest Most Popular More Commentary. Quick Links Services Account Types Premium Services Zacks Rank Research Personal Finance Commentary Education. Resources Help About Zacks Disclosure Privacy Policy Performance Site Map.
Client Support Contact Us Share Feedback Media Careers Affiliate Advertise. Follow Us Facebook Twitter Linkedin RSS You Tube. Zacks Research is Reported On: Logos for Yahoo, MSN, MarketWatch, Nasdaq, Forbes, Investors.
What is Derivatives Market & How to Trade in Derivatives | Kotak Securities®
Logo BBB Better Business Bureau. NYSE and AMEX data is at least 20 minutes delayed. NASDAQ data is at least 15 minutes delayed.